Introduction:
CDMA means Code Division Multiple Access; this system uses a technique called the multiple accesses. For various technologies such as radio communication technologies this system is useful. This system has the spread spectrum technique; in this the data bandwidth is spreader by the code uniformly. In such time the transmitted power is same. For all the codes of the user, the codes which are spreading are orthogonal.
This spreading code has its own specifications. Here the user’s code is generated by Gold codes, Walsh codes, and generation of the PN sequence. For modeling of this CDMA systems use the different approximations types such as Improved Gaussian Approximation (IGA), Gaussian Approximation (GA), and Simplified Expression for Improved Gaussian Approximation (SEIGA).
In this, by using the Gaussian Approximation (GA) CDMA is modeled. When ever using the CDMA with GA in that situations keep the approximations of interferences and the channel noises are at zero because, the random variables of the Gaussian with certain variance of Gaussian. For describing the following, fading is used. Those are the amplitude’s rapid fluctuations, the radio signals multipath delaying or phases or distance of travel. This is done because at various times, the interferences are living in between the transmitted signal of two or more versions.
At receiver side the result of this is varying of the same signal amplitude and the phase. The shadowing result is slow fading, this is done because of the mountains, buildings and differ other objects. The occurrence of the shadowing is done when at the power of received signal the mobile experience the reduction. This is possible when the mobiles moved to the behind of obstruction.
The Lognormal Fading Channel is considered for the proposing system. According to the distribution of Lognormal, randomly this channel fades the transmitted signal amplitude. The channel coherence time is large when compare it with the channel delay constraints in that situations the fading channel of Lognormal is considered as slow fading.
Motivation:
The various services are supported by the wireless multimedia system. The supporting of these services is done with various performances of delay and the error and also the transmission rates at a wide range. The structure of the network has the following such as terminals, mobile handsets, broadband network, base stations and control entities. In this the terminals means data, low rate video, image and voice. The broad band network is used for the base stations connections. This broadband network is possible either with the wired connection or wireless connection. The following is the figure shows the connection of broadband network in both the point of view such as in wired and in wireless.
At the subnet of wireless, at the mobile/fixed user initiating or terminating the communication link from base stations to the broadband network. At different times the transmission id takes place. First the transmission is taking place in between the mobiles and the base station, this is known as uplinks. And next transmission is taking place in between the base station to the mobiles, this is known as the downlinks. This is possible either in between the same radio channels or different radio channels. If this is in various or different radio channel then it is called as “Frequency Division Duplex FDD”, and if this is in same radio channel then it is known as “Time Division Duplex TDD”.
The following is the table shows for different multi media services requiring bandwidth in the downlink and uplink of the wireless network.
| Multimedia Services | Downlink Bandwidth | Uplink Bandwidth |
| Broadcast VideoBroadcast TVEnhanced pay per View | 1.5 – 6 Mbps/ channel | None |
| Interactive VideoVideo on DemandInteractive TVInteractive GamesInformation Retrieval Services | 64 kbps – 6 Mbps | 9.6 – 64 kbps |
| Internet (www, ftp, telnet)Voice | 14.4 kbps – > 10 Mbps | 14.4 – 128 kbps |
| Symmetric dataDesktop multimediaWork-at-homeVideo ConferencingVideo TelephonyFax | 9.6 kbps – 2 Mbps | 9.6 kbps – 2 Mbps |
| Small Business/HomeInternet Home pageInternet Information Server | 9.6 – 384 kbps | 64 kbps – 1.5 Mbps |
Table: the transmission rates of the uplink and downlink in the multimedia services.
Over the mobile when the signal is under the transmission, such signal has more attention because may occur the shadowing and the path loss. These are might be occur because of the uncertain such as buildings, terrain, and any other. These are very much larger when compare this to the radio channel frequency’s wave length, the result of this is faded of multiple paths and the channel with time variant.
That means the signal which is received has the variations in the power and randomly it will be fluctuated. If the power level which is of same, at this if all the mobiles wants to transmit in that times the receiver mobile which is near of this signal, at strong level this is received. If the receiver which is far away of this signal, at weak level this will be receive.
This type of effect is known as “near-far effect”. If the power levels of the received signal has the differences in the range of the 80 ~ 100 dB then the result of this is causing the cochannel interference with more amount and saturate the receiver’s weaker signal.
At very low rate the utilization of the frequency spectrum of current mobile system is there. According to the estimations of the optimistic, the fall of the highest achievable capacity of mobile systems of second generation 20 percent under the capacity of the Shan-non channel. In order to close the capacity of the channel in real system, the more diversity paths are used by the wideband mobile system capacity.
To all the users started the radio channel of the common wideband, because of this the CDMA wireless system will became the potential candidate for the mobile communications which are having the high capacity. The standard bodies of wireless communication systems in Europe, Asia, and North America proposed that CDMA for the wireless systems of third generation is as “major multiple access technique”.
In order to lighten the near-far problem, develop the algorithms for the power controlling. This is done at the receiver of base station compensate the fluctuations and variations of signal power of a mobile. The adjustment made to the power will leads to the increment of the system capacity. This increment is done in terms of same number of calls. In CDMA, the limiting factor is level of total interference for the capacity of the system; in this the frequency and the time of the radio channels are not separated.
If the single user uses more power then it will automatically reduce the communication capacity of the other users. This reduction is done in significant manner. So, here in CDMA the most essential and important are management of resource and the power control. In so many investigations, the uplink power control of the CDMA is treated as main focus because the signal of the user cell experiences the characteristics of various channel by the following of the propagation path of various.
On other hand, the downlink path desired signals and the interference of the intra-cell are under doing the impairments of the same channel and preserve the relative power levels. If, on the basis of the single cell, if the noise of the background is negligible at that time the power control of the downlink is no need. Where as in case of the multi-cell, in this should employee power control of the downlink. But in this the power control of the uplink is more complicated.
Besides the hostility of the near-far problem, in order to accommodate the various Qualities of Services (QoS) the power control is engaged in terms of BER (Bit Error Rate). For maintaining the BER which is targeted, processing gain increment, or decreasing the equivalent transmission rate maximum power fails available if the channel condition id poor. This is improved further in terms of average “signal-to-interference ratio” and the BER.
In other hand it was proposed in this research here the rate of data will be regulated in the way that requirement of delay performance of a multimedia CDMA system is controlled as a task of the resource (rate and power) budgets. It is highly advantageous to mange the resources of network efficiently so that the QoS needs for user is satisfied and it uses network resources maximally.
A significant factor in assigning power as well as data rate to mobile is the assignments of base station it resolve the access point of the mobile to network of wireless. In other words allocated resources may differ with various assignments. Traditionally a mobile user is linked to the closest base station or to the one where broadcasted signal of pilot is sensed as the strongest that implies that the route from the mobile to this base station is the greatest with respect to all additional base stations. The latte and performer assignment is one of the least signal attenuation (LSA) assignments. In the absence of fading and shadowing where NBS assignment is valid.
If the traffic is evenly distributed across the total network consequently every base station sees the same entire interference at its getting antenna. LSA assignment offers maJcimum SIR, therefore the best performance .Moreover a base station is having high local t r a c ,in spite of being the Choice, may take a mobile signal with a Iowa level a than a near base station with a lighter local traffic. So an equipment decision based on the global traffic at least in a dust of near base station outperforms the MA.
It is interested in exliming the performance of globally decided assignment which is compared to the LSA; here it combines the assignment with the allocation of resource. Optimization methods are employed commode in the literature for cellular management system and power control.
The algorithms of power control HMS are stated for mobile system s of narrow band to minimize the entire transmitted power and this enhances the system capacity. Many of the algorithm are planed for traditional voice communication as well as do not tackle various rates and quality of service for various users, as for the system of CDMA, relevant architectures are focused on transmission rate and BER requirements of real time services.
Moreover non real time forces with different requirement of delay had not been tackled. However stated models are restricted to single-cd environments where as roaming problems as well as linked challenges like base station is disregarded.
Results:
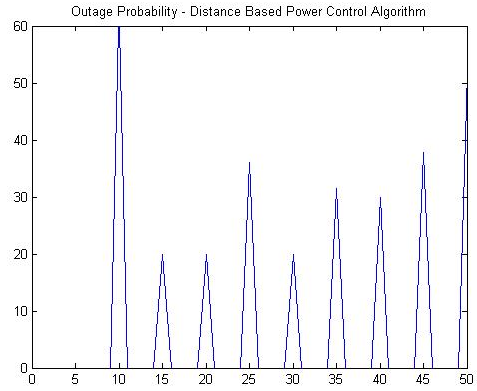
This figure shows about the distance in the power control algorithm in the outage probability when the system is in the CDMA.
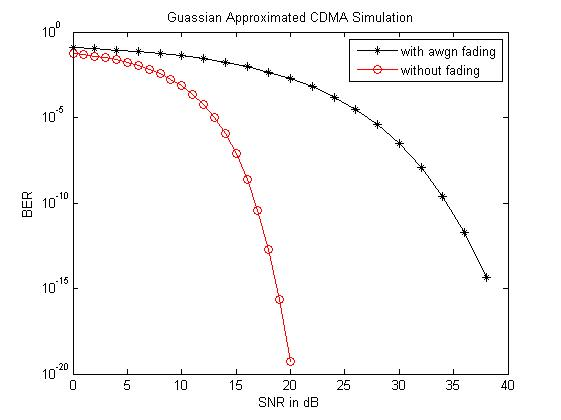
Figure 2: Comparison of performance of Gaussian Approximated simulation of CDMA
The above figure represents SNR versus Signal to Noise ratio in dB for performance of the Gaussian approximation values of CDMA without and with awgn fading. In clear, the system without awgn fading when compared to the system with awgnl fading performs better for SNR’s highest values.
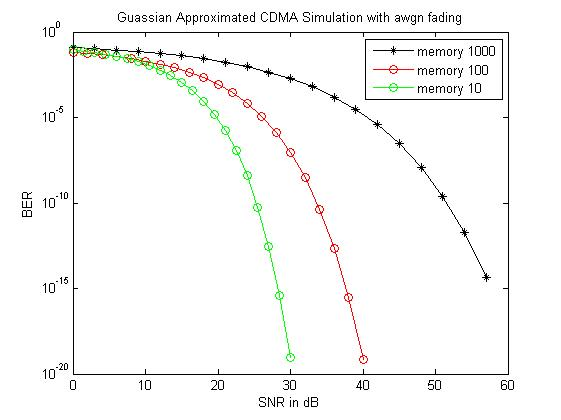
Figure 3: Comparison of performance of Gaussian approximated CDMA simulation with awgn fading.
The above figure represents SNR (dB) versus BER for an A-CDMA system for different values of memory of channel with awgn fading. As the memory of channel enhances, in fading the rate of change reduces, and thus the BER reduces.
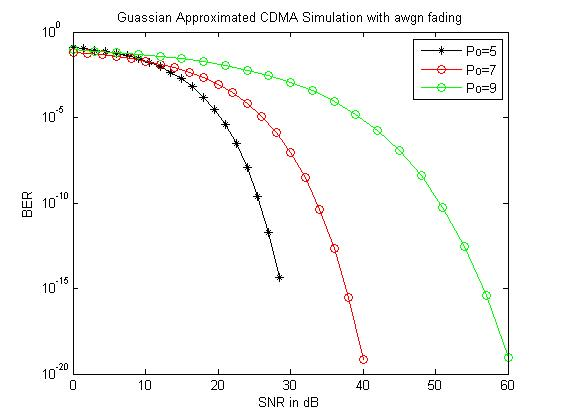
Figure 4: Performance comparison of Gaussian approximated CDMA simulation for the case of awgn fading with different user 0 powers.
The below figure represents the SNR (dB) for Gaussian approximated CDMA simulation with awgn fading for various values of user 0 power. At present, the level of power of interferers is proportional directly to the 0 user power, so that CLT (Central limit theorem) can be integrated to estimate the interference contribution with a non-unity Gaussian variance as zero mean Gaussian distribution. Thus, the interferer powers enahnce as user 0 power enhances.
Conclusion:
The performance of Gaussian approximated CDMA simulation system is compared with awgn fading in this paper. Obviously, the case of awgn fading performs poorer when compared to no fading case. In addition the performance of Gaussian approximated CDMA simulation system is related for various cases of memory of channel. Faster is the rate of change of fading, if lower is the memory of channel, and thus the rate of BER also improves.
The interferer power is higher if the user 0 power is higher, and therefore the rate of BER also improves. This research’s most significant accomplishment is to attain a simulated BER of the order of 10 seconds or less for Gaussian approximated CDMA simulation system by making use of MATLAB.

PLS FORWARD THE CODE YOU HAVE FOR THIS PROJECT FOR REFERENCE