Abstract
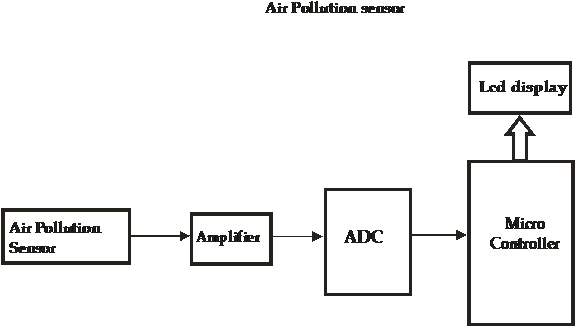
The aim of this Rocker Bogie Suspension System project is to develop a surveillance robot for defense which is capable of moving in all surfaces and is capable of driving in rock terrains and live video streamlining with help of a camera.
This robot has a special mechanical structure which is capable in driving rock terrains which is only possible with chain robot, but chain robot has some bugs and to overcome those bugs we designed a mechanical structure as following in figure
Coming to the mechanical structure of this robot it contains 8 wheels which are derived with DC motor and these motors are fixed to aluminum plates which are 220mm length, 30mm width, and 3mm thickness this has 12mm drill in the center for fixing C shape wing.
The shaft in the center is for balancing the mechanical structure for either side of robot There is push rod mechanism on either side of the robot which is helpful in limiting suspension height when driving terrain rocks which is also adjustable manually as per the requirements.
In this project we used some aluminum material as well as metal steel depending on the mechanical structure where it needs more strength and weight in particular area used metal steel material and remaining place aluminum is being used.
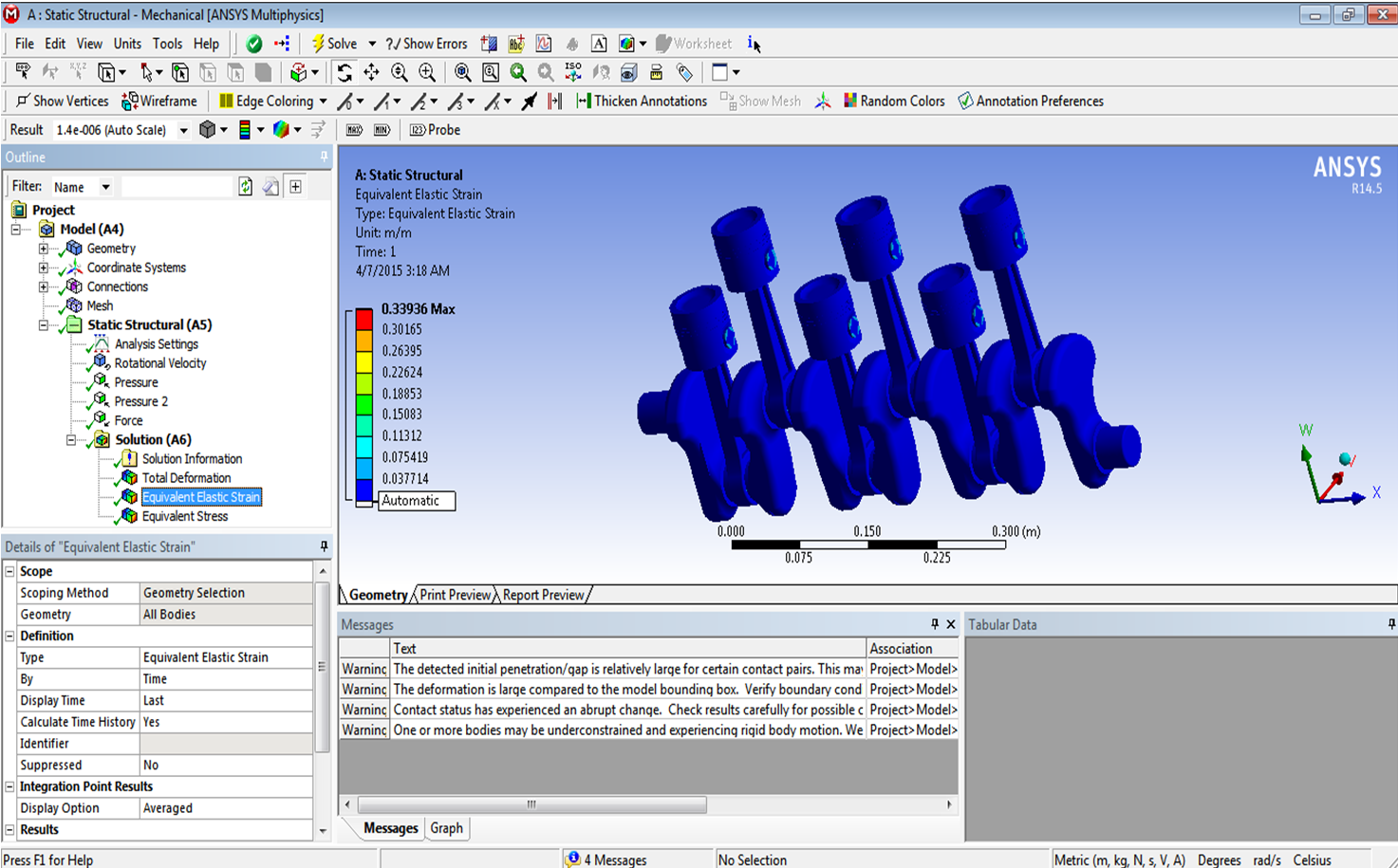
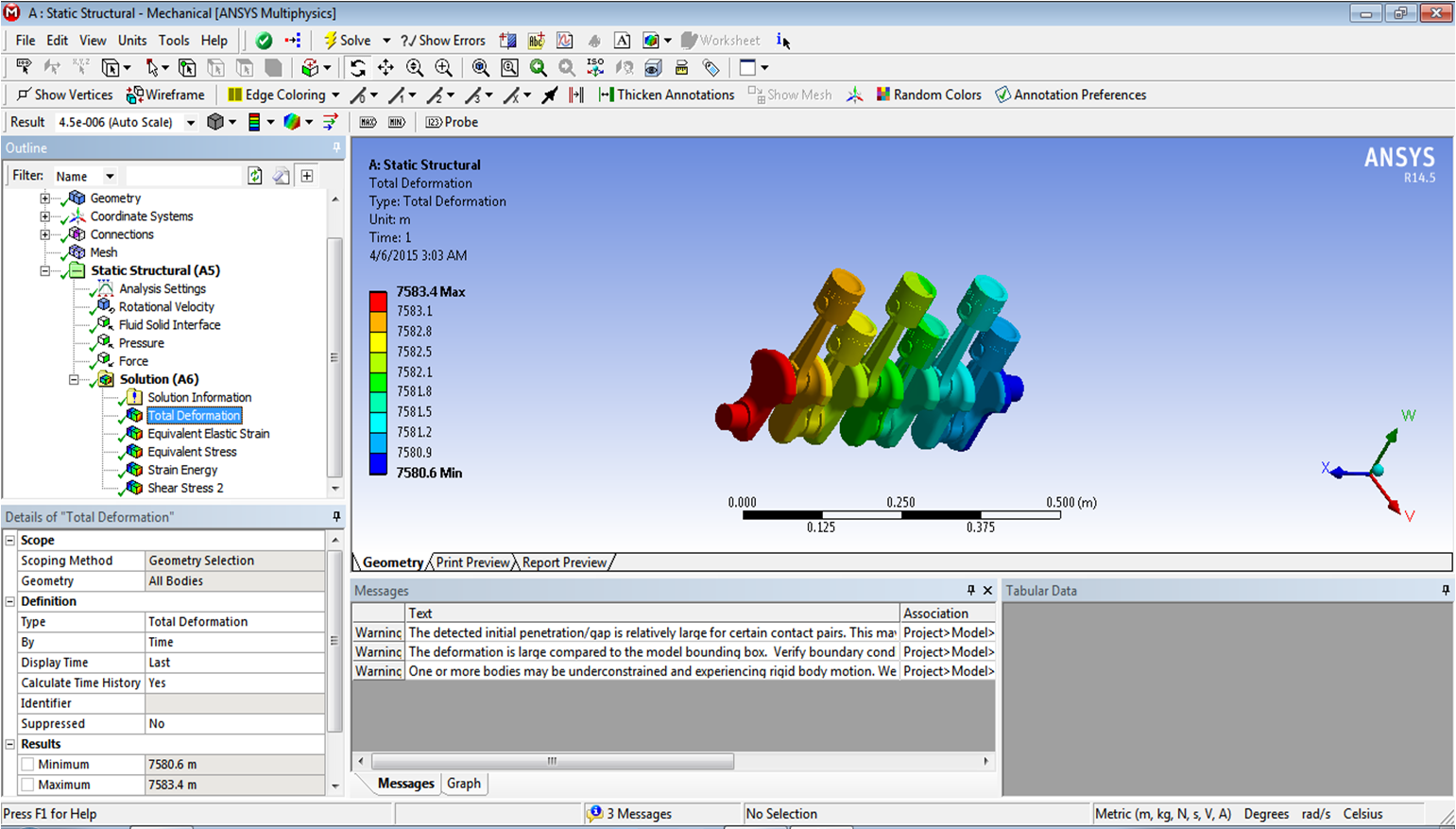
This is the Rocker-Bogie Suspension System with the dual bogies and this has the rocker in between to protect the vehicle from over collapsing
- Existing model was in 6 Wheels
- Proposed System is with 8 Wheels which can protect itself from over falling
- This can be controlled via the android app with the help of Bluetooth Network.
- This can be navigating multiple terrains in uneven surfaces can travel in mud areas
- We have developed the entire robot in MS Sheet.
- The below Project is solar based Rocker-Bogie Suspension System with Gripper attachment.
- The previous one is for surveillance Purpose and this one for pick and place operations