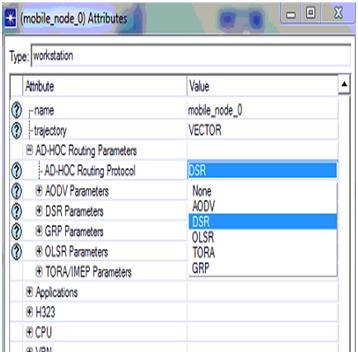
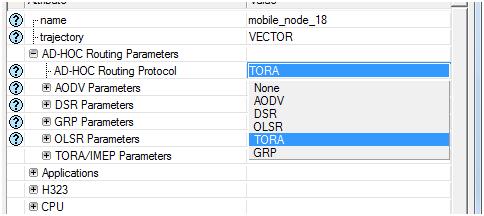
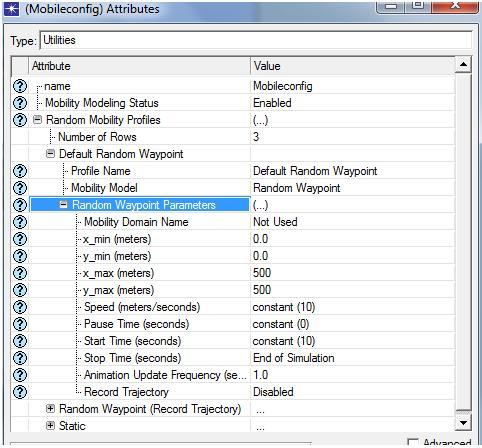
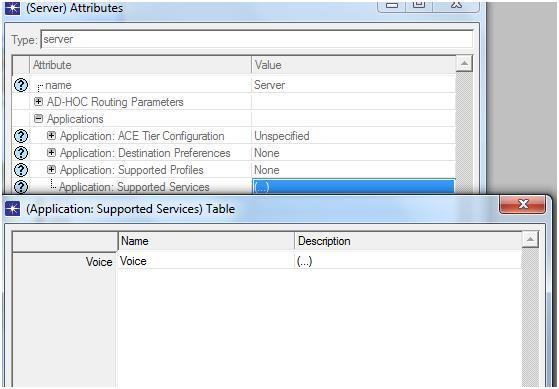
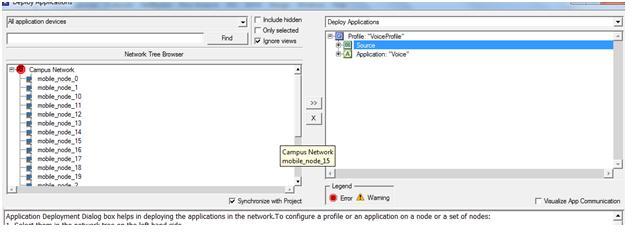
Simulation tool:
As discussed in the introduction section of this chapter the simulation procedure of this application considers two scenarios and the simulation tool used for simulating the scenarios is OPNET modeler. In comparison with different simulations tools like OMINET and NS2, OPNET modeler is considered as the best simulation tool as it provides several advantages that they cannot provide.
The significant advantages of OPNET modeler are it supports level of models and provides a user interface to establish several networks. Not only OPNET modeler, NS2 is also considered as a best simulation tool but the single disadvantage in using NS2 is its behavior which is very complex as it includes loads of coding part and this problem is completely avoided using the OPNET modeler.
The significant factor that encourages the usage of OPNET modeler is its drag drop approach, using this approach the simulation procedure is done very simply by selecting the required objects from the object palette that is available by using the OPNET and the configuration of the objects is also provided, the other important feature of OPNET is it supports several model families over the wireless network to enable the communication.
The network setup required for the simulation can be completed by dragging the required objects from the object palette and then by configuring them according to user’s requirement. The model of the simulation includes the operations like establishing the network needed, checking the consistency of the model, simulation running and at last estimating the results.
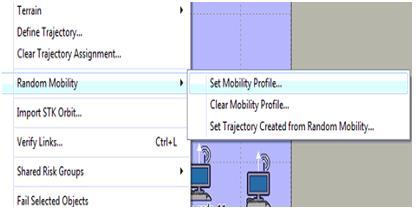
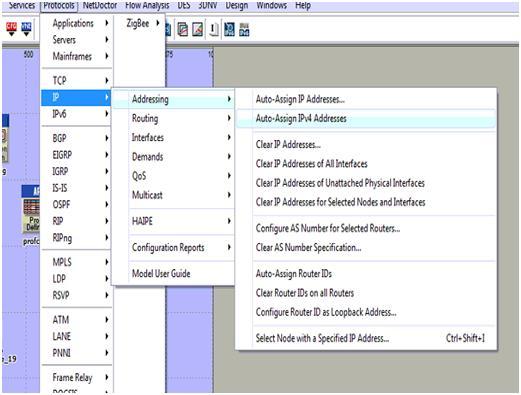
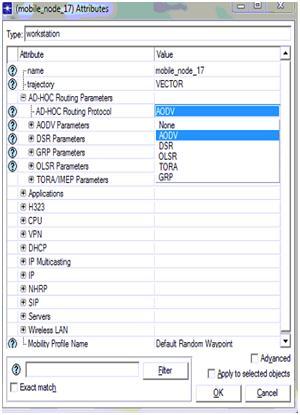
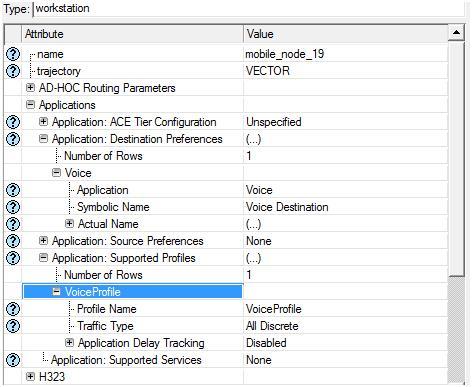
Irrespective to the type of network to be created these steps are followed in creating the wireless and wired networks. Because of this reason OPNET is regarded as the simple way out to create any network. In addition to the above models of networks, latest network technologies are also provided by OPNET such as the Mobile Adhoc networks, Zigbee networks and wireless mesh networks. Using these available models the estimation of network’s performance can be done easily.