Asynchronous Transfer Mode Seminar Report Over View:
Asynchronous Transfer Mode provides high performance, multiplexing technology and cell oriented switching. It utilizes the fixed length packets in order to carry the various kinds of traffic. It enables efficient applications of multimedia and high speed connection of LAN. High range networking decks are also used.
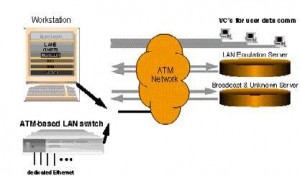
Some of the advantages of ATM are as follows:
Compliance with the international standard
Use of dynamic bandwidth
Supporting multimedia
Speed scalability
Network size
WAN architecture
Simplification opportunities via the VC architecture
ATM classes of service include:
Available bit rate
Unspecified bit rate
Constant bit rate
Variable bit rate
The technical parameters of ATM include:
Burst tolerance
Sustaining the rate of cell
Rate of the peak cell
Variation in the delay of cell
Delay in transfer of cell
Loss ratio of cell
There are two standards for ATM networking and it includes:
Public network-to-network interface
Broadband interface
It provides service from end-to-end.
A standard ATM is interworking between the frame relay and ATM.
These are set of specification that provide a stable framework for ATM.
Schemes of data insertion
The traffic of interrouter specifies the function of RFC1483 which is encapsulated.
LANEMPOA supports the use of ATM SVCs.
Voice and video adaptation schemes-nit provides efficient traffic that does not break the natural system like that of the circuit that helps in carrying the bits at a perfect rate.
Two modes can occur with the coding of MPEG2:
Program streams that varies in packet length and carry multiple as well as single programs.
Transport streams include 188 byte packets which consist of several programs.
MPEG2 is used for the insertion of time stamps during the process of multiplexing and encoding in order to make more perfect use of the resources of the networking. To free the bandwidth various techniques of dynamic compression as well as alleviated congestions are used.
