DATABASE: Database is a “collection of interrelated data”.
Ex: Sales D.B contains Sales data for ex: consumer’s products etc.
DATABASE TYPES:
1. OLTP: It is simply called Database
2. OLAP: Data warehousing.
D.B:
-“Organizations Creates Database is to keep details about day to day transactions”.
-The Basic Operators Performed on Database are
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- SELECT
DBMS : {Database Management System}
System: software (or) set of tools.
It is a software to manage Database.
- DBMS is an interface between user & Database.
- DBMS is also called as “Database Server”.
- Database is introduced in 1970’s.
- FMS introduced in 1960
- HDBMS and NDBMS introduced in 1970
- RDBMS introduced in 1980
- ORDBMS and OODBMS introduced in 1990
Files & FMS:
File Management System:
- Data stored in files & data managed by using FMS (or) FPS (File processing System)
- Examples of FMS is COBOL Language.
FMS
- More Redundancy (Duplication of data)
- More Inconsistency
- Less security
- Lightly Development
- It doesn’t support DATA INTEGRITY RULES
DBMS
Less Redundancy (Because Of DBMS Follows the Normalization)
- Less inconsistency
- More security
- Rapid Development Fast {Some tools Have DBMS i: e. RAD tools rapid Application development}
- DBMS supports “DATA INTEGRITY” Rules
- Primary key
- Foreign key
- Unique Key, etc
DBMS TYPES:
Outdated DBMS Types are
- HDBMS
- NDBMS
Presently used DBMS Types are
- RDBMS
- ORDBMS
- OODBMS
These are all based on “DATA MODEL”
DATA MODEL:
- Model means representation of data.
- Data representation can be
- Hierarchical Data model
- N/W Data model
- Relational Data model
HDBMS:
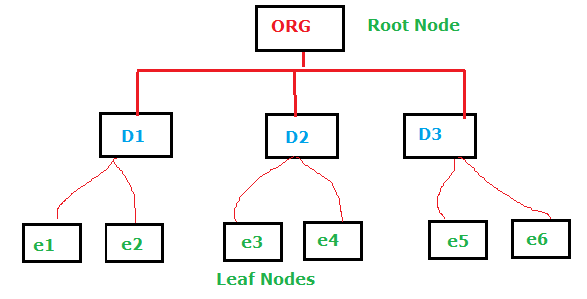
- In HDBMS DATA Represented in the form of inverted tree.
Example: IMS [Integrated mgmt System] introduced by IBM.
Disadvantages:
- This supports only one to many relationships.
- It doesn’t’ support many to many relationships.
- Data retrieval is slow.
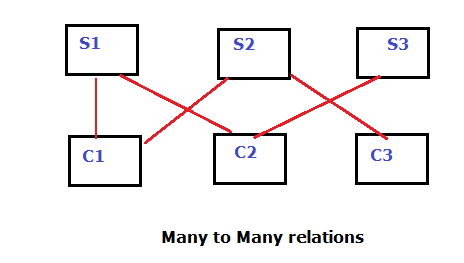
NDBMS:
- It supports all types of relationships.
- In NDBMS data represented in the form of “Nodes”
- Ex. Of NDBMS is IDMS [integrated database mgmt system]
- IDMS introduced by IBM
Disadvantages:
- Complexity relationship.
- Data retrieval is slow.
- This model is introduced by “E.F.CODD”
- He designs some rules are called “CODD Rules”
- 12 Rules are designed.
- A dbms which data file all CODD rules is perfect ”RDBMS”.
Rule (i): Information Rule:
- Data must be organized in 2d tables.
Table: Collection of named columns & unnamed rows.
Ex: Empid Ename Salary
1 A 500
2 B 600
- Vertical Columns are also called Fields (or) attributes.
- Horizontal rows are also called records (or) tuples.
- Intersection of row & column must be atomic [single].
- Records are uniquely identified by “primary key”.
- Tables are related using “foreign key”.
Examples of RDBMS:
- SQL SERVER
- ORACLE
- DB2
- MYSQL
- SYBASE
- INGRES
- INFORMIX
- TERADATA.
The first RDBMS is called “system R”. It is introduced by IBM.
ORDBMS:
- Which stands for obj. relational DBMS?
- ORDBMS= rdbms + OOPS
- It is not a new system; it is an extension of RDBMS.
- User defined Types [UDT] is introduced by ORDBMS.
Address {
House No
Street
City
State
}
- Examples of ORDBMS are SQL SERVER, ORACLE.
OODBMS:
- It is extremely based on “oops”.
- Here data is represented in the form of “classes &Objects”