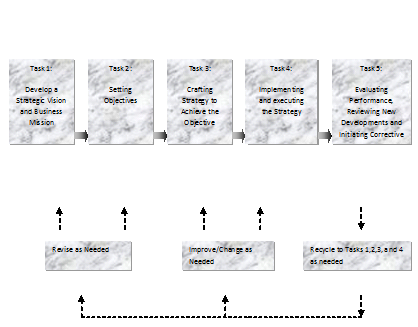
Strategy implementation
“Strategic implementation is regarded as a form of organizational learning wherein the threats and opportunities are studied to come up with new strategies in response to such threats and opportunities. This makes the organization to finetune its strategies according to the environmental factors which is a constant learning process.”. It is inferred from the above discussion that strategy implementation is a tough task for management as it is an art of making people to do the work in line with the strategy. So, only strategy implementation is regarded as a sort of expertise.
The various prototype factors in the course of strategy implementation are generally soft, hard and mixed. These depend on the level of communication with the people around in the organisation. Strategic implementation is largely influenced by the mechanism employed for co-ordination. Strategy execution implies a step by step approach to implementing certain activities that lead to a formulated and structured decision making. It is regarded as a cognitive process.
The key to success lies in the effective mapping of the necessary outcomes with performance measures. The general trait of successful leaders is that they share their vision among the team members in the form of simple stories about their visionary and the hallmark of the success is attributed to the celebration of their achievements or milestones whether big or small.
To see that the strategy is shared, the team should openly voice their opinions about the strategy, confront premises, and challenge the theory and propose alternatives without fear of being scolded. The successful strategic implementation call for leaders who can inspire and mould through coaching rather than command and control. Recognizing success and granting appraisals based on their performance, inspiring and motivating them lead to better results in inducing better commitment rather than by using force and authority which contribute to cold rebellion and inactive resistance.
In tune with this discussion, strategic planning is interpreted as primarily an analytical process that aims at the selection of long-term goals and objectives that appropriately enables to design a sophisticated organization structure. A notion is that desired outcomes could be achieved by focusing on both internal and external factors and analysing them by the means of professional management to implement strategic actions. Effective planning can minimize the consequences of uncertainty.
The possibility is not encouraged that : leaders or planners do tend to overlook the new potential opportunities attributing to their previous history, their ability or experience; that design of novel proposals might be disrupted due to the political factors prevailing in the corporate culture, transient market conditions; that planning overlooked the lower hierarchical knowledge and expertise to consider only the top hierarchy decisions; that planning entertained strict adherence to the plan, giving less room for flexibility and learning . Nevertheless, as outcomes deviated from the desired intentions, as strategies could not succeed in delivering the desired results pertaining to the organizational motives and as plans often remained futile without serving any purpose just to remain unused on the top shelf, people started to refine the planning model.
Steadily, the recognition emerged that formal planning contributed least in the successful results and effective strategic decisions and the belief of synchronizing the internal factors of the enterprise to the external environmental conditions is deemed to be too shallow . It is not successful in realizing how internal organization operations and sub cultures were loosely bonded, how divergence, chaos and dissimilarities lead to novelty in innovation and rediscovery, and how persistent response to the swift changes provokes instability, unfair outcomes and failure to remain core competent. Three primary ideas dawned to form thinking on what is required to overcome these loopholes in how the strategy process was framed.
The first postulated Michael Porter’s proposal that business strategy should give rise to greater performance, competitive positioning, sustainable competitive edge, and commitment to a determined path. The second from Henry Mintzberg who stated that the strategic outcome is a lot influenced by the organizational design and structure, political and cultural environment or the gradual strategic formation based on the managers’ reaction to the external pressures pertaining to the external competitive surroundings. The third proposal comes from Hamel and Prahalad who viewed core competencies and potentialities as the prime factor for competitive edge.
Chaffe proposes that strategy is multi-faceted and dependant on the situation. Nevertheless, he says that it suffers from three conflicting aspects of strategy. The first model is the linear strategy model which is largely centered on forecasting and development and the second one is the adaptive strategy where the managers’ prime focus is on the means and the third one is the interpretive strategy where the procedure of research goes on the lines of the qualitative opinions of the people that reflect reality.
Conventionally, a strategy is implemented by the top level management and is passed through the next successive levels of management . For instance, in the case of successful coaches and top directors where the rules are set to be followed by the players or employees at the right time. The functioning of the strategy closely resembles the relay team which comprises of four legs and the baton is passed from the first leg to the fourth leg. Likewise, management is composed of four management hierarchies namely the senior management, middle level management, the low level management and the non-management level .
The strategy is framed by the senior level management and the middle level management and is made to be followed by the low level management and non-management like how the baton is passed in a relay from the first person to the fourth person. If the senior or middle level management is not clear in implementing or communicating the strategy, it leads to confusion and chaos. Moreover, when the involvement of senior management is too low in implementing the strategy, it takes a lot of time to reach the non-management level which leads to the failure in strategy.